If your dog suddenly isn’t interested in food, it can be pretty concerning. As pet owners, we’re used to seeing our dogs eagerly waiting for their next meal, so a shift in appetite might leave us wondering: how long can they actually go without eating? & When to worry if a dog won’t eat. Let’s find out;
1. Understanding How Dogs Handle Food & Fasting
Dogs, just like us, need a balanced diet to stay healthy. They rely on nutrients from protein, fats, and some carbs to fuel their day, keep their coats shiny, and keep those tails wagging. Without food, they start to dip into their energy reserves, which isn’t ideal long-term. Dogs actually have a faster metabolism than we do, so they may feel the effects of going without food sooner than we would.
Quick Expert Insight Veterinarian Dr. Jennifer Coates explains that while a healthy dog might manage a short fast, prolonged food deprivation can cause issues—especially if they’re not drinking enough water.
2. How Long is ‘Too Long’ for Dogs Without Food?
Healthy Adult Dogs If they’re otherwise fit and healthy, most adult dogs can manage 3–5 days without food if they’re still drinking water. But, just because they can doesn’t mean they should.
Puppies and Senior Dogs These guys are more vulnerable, so they can usually handle only 24–48 hours before it becomes a concern.
Sick or Underweight Dogs For dogs who aren’t in the best health, even a day without food could be dangerous.

| Dog Type | Time Without Food |
|---|---|
| Healthy Adult | 3–5 days |
| Puppy | 24–48 hours |
| Senior | 1–3 days |
| Sick/Underweight | 24 hours or less |
3. Factors That Affect How long can a dog survive without food
While writing about dog without eating for long feels uncomfortable to me. Loving a dog like our baby I always prioritize feeding him on time however, there comes some situations that they resist eating. Every dog is different, and there are a few key factors that impact how long can a dog live without eating:
1.Size and Breed
Large breeds might handle food deprivation a bit better than smaller ones due to their size and metabolism.
2. Age
Pups and seniors have a different chemistry, pups are active with fast energy consumption while adults are weak and have less effective metabolism. Puppies and senior dogs are more sensitive to going without food—they need consistent nutrition.
3. Health Condition
If your dog has a health issue like diabetes, they may need food on a regular schedule to avoid complications. Also diabetes evoke more hunger-pangs so a constant feeding schedule is necessary.
4. Hydration
Dehydration is a bigger immediate risk than hunger. If your dog isn’t eating, make sure they’re at least drinking water to stay hydrated. Hydration will keep them active and help them survive longer.
5. Environment and Stress
Situations like fear, threat or a trip to the vet can sometimes cause appetite loss, but it should bounce back once they’re calm again.
4. Signs That Going Without Food is Taking a Toll
Signs and Stages of Fasting-Related Health Issues
If your dog isn’t eating for a day or more, you may start noticing changes in their energy, appearance, and behavior. These signs vary depending on how long they’ve been fasting, as well as their age, health, and hydration levels. Here’s a closer look at what to watch for:
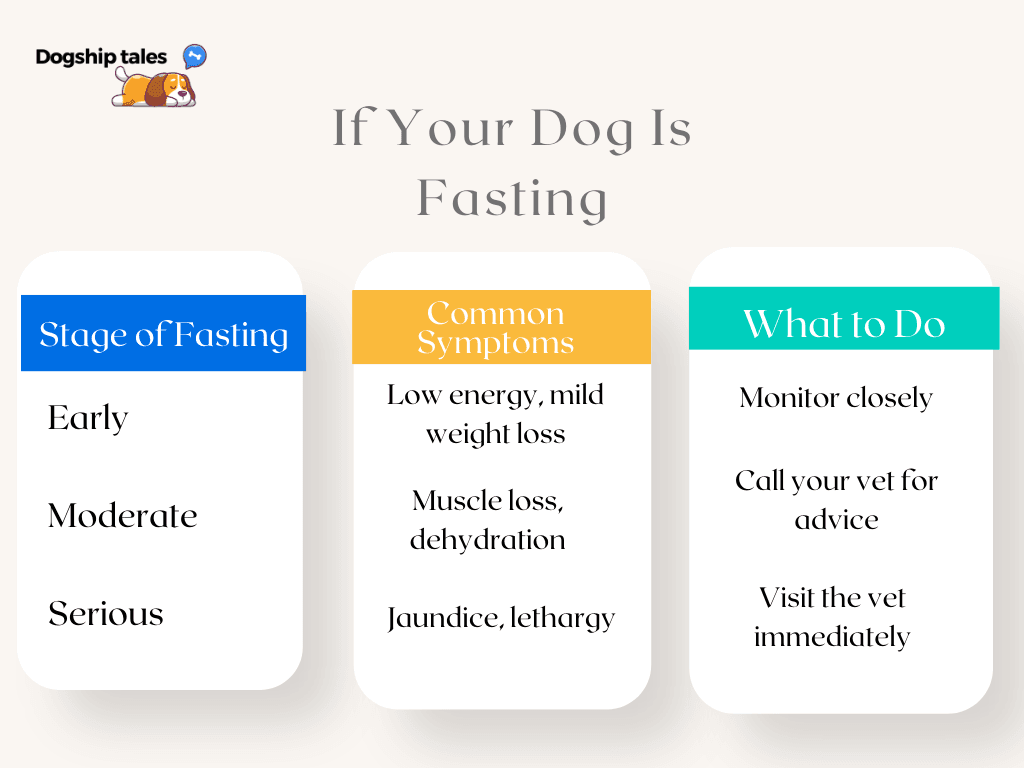
1. Early Signs: Low Energy and Mild Weight Loss
When a dog skips a meal or two, it might not be immediately obvious that they’re fasting. However, if it continues for more than a day, you might notice:
- Lowered Activity Levels: Dogs tend to get a bit lethargic without their regular nutrition. You might see them lying down more than usual, avoiding play, or seeming uninterested in their usual activities.
- Weight Loss: This won’t be dramatic at first, but over a couple of days, you might see slight thinning, especially around their ribs or waist.
- Behavioral Changes: Dogs that are hungry for extended periods may also seem “off,” possibly more irritable, withdrawn, or less interactive than normal.
What to Do: During these early signs, it’s a good idea to monitor their eating habits closely. Offer small, easy-to-digest foods like boiled chicken or broth to see if their appetite picks up.
2. Moderate Signs: Muscle Loss and Dehydration
If fasting continues beyond 2–3 days (or even sooner for puppies, seniors, or dogs with health issues), more noticeable effects will begin to show, including:
- Muscle Loss: Without food, the body starts breaking down muscle tissue to meet its energy needs. You might notice your dog looks skinnier overall, with less muscle tone, particularly around the limbs.
- Dehydration: Dehydration quickly becomes a concern, especially if your dog isn’t drinking. Watch for signs like dry or sticky gums, thick saliva, and lack of skin elasticity (you can check by gently pulling up on the skin between their shoulder blades—if it doesn’t snap back quickly, dehydration may be an issue).
- Digestive Issues: Some dogs start vomiting bile or experiencing nausea when they go without food. This can be especially uncomfortable for them and is a sign they need food soon.
What to Do: At this point, consult your veterinarian to rule out any underlying health problems. Encourage your dog to drink water or broth, and discuss appetite stimulants or options to prevent further fasting effects.
3. Serious Signs: Jaundice and Neurological Symptoms
If fasting continues, serious and potentially life-threatening signs can develop. In this stage, your dog’s health is severely at risk, and immediate intervention is crucial. Look for:
- Jaundice: This can show up as yellowing in the gums, eyes, or skin, and is a sign of liver distress. Jaundice indicates that the liver isn’t able to process toxins properly, often due to prolonged lack of nutrients.
- Neurological Symptoms: Prolonged fasting affects blood sugar and other metabolic balances, which can lead to wobbliness, disorientation, or confusion in your dog. These symptoms indicate that vital organs, including the brain, may not be receiving adequate energy.
- Severe Weakness or Collapse: If your dog seems unable to stand or has trouble moving, they may be on the verge of collapse from weakness or low blood sugar. This is an emergency situation.
What to Do: If you observe any of these severe signs, seek emergency veterinary care immediately. At this point, the dog’s body is not able to cope without intervention, and they may require fluids, supplements, or even a feeding tube to restore essential nutrients.
5. Why Hydration is Critical
Here’s the thing: water is even more important than food when it comes to survival. Dogs can go longer without food than without water, and dehydration can quickly turn into an emergency. If your dog isn’t eating, try to encourage them to drink water or low-sodium broth. I will also write about “How long can a dog go without water” to discuss how hydration is so critical and extent of dehydration a dog can bear.

Hydration Hacks
Add a splash of low-sodium broth to their water bowl.
Offer them ice cubes to lick or chew. Also see what they can drink besides water.
Monitor for signs of dehydration, like dry gums or skin that doesn’t “snap back” when pinched.
Must check out this research: Why you should give Low Sodium Broth to your dog.
6. Why Your Dog Might Stop Eating in the First Place
Medical Issues: Common causes of appetite loss include dental problems, digestive issues, or infections.
Behavioral Reasons: Stress or anxiety from a new environment, a change in routine, or even boredom with their food.
Diet Preferences: Some dogs are particular about their food—if you’ve recently switched their diet, it could take a few days for them to adjust.
Vet Advice: Dr. Sarah Wooten says it’s always best to rule out medical reasons first if your dog stops eating. Sometimes, what we think is a “picky eater” might actually be a dog with a health issue.
7. How to Encourage Your Dog to Eat Again
If your dog has gone a day or two without eating, here are a few tricks that might help get them interested in food again:
1. Bland Diet
Start with something easy on the stomach, like boiled chicken and rice. You can gradually add their regular food back in as they get their appetite back. Until then try to give them limited amount of flavored canine treats.
2. Appetite Boosters
Try warming up their food to make it smell stronger or mixing in a small amount of low-sodium broth. Broth is one of the most favorite drink/meal for dog so its aroma will evoke their hunger back.
3. Appetite Stimulants
Ask your vet about how long can a dog go without eating, they will guide you according to your dog breed. They may suggest appetite stimulants to help your furry friend come out of fasting mode too.
4. Keeping Your Dog’s Appetite Steady
To help prevent fasting episodes, here are some simple tips:
Regular Feeding Schedule: Dogs love routines! Try to feed them at the same times each day.
Balanced Diet: Make sure their food meets their nutritional needs, as this can prevent some health-related appetite issues.
Regular Vet Visits: Routine checkups can catch health issues early and keep your pup healthy and hungry.
Conclusion
While most healthy dogs can go a few days without food, it’s always better to get them eating again as soon as possible. Puppies, seniors, and sick dogs can’t handle as much time without food, so keep a close eye on them. If you notice any concerning signs or if your dog hasn’t eaten for more than a day or two, it’s time to reach out to your vet.
Remember, if your dog isn’t eating but is still drinking water, that’s a good sign. And when in doubt, consult your vet—they’re your best resource for keeping your furry friend happy, healthy, and well-fed.
Additional Resources
ASPCA: [Dog Nutrition and Health]
American Kennel Club (AKC): [Feeding and Fasting Guidelines]
Veterinary Partner: In-depth resources on canine health and diet.





